Cyzicus
From Textus Receptus
(Removing all content from page) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
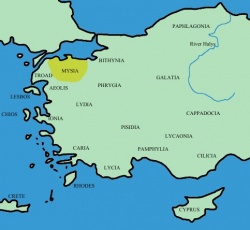
| + | [[Image:Mysia map ancient community.jpg|thumb|250px|Cyzicus was a town of Mysia.]] | ||
| + | '''Cyzicus''' ({{lang-el|Κύζικος}}, ''Kyzikos''; {{lang-ota|آیدینجق}}, ''Aydıncıḳ'') was an ancient town of [[Mysia]] in [[Anatolia]] in the current [[Balıkesir Province]] of [[Turkey]]. It was located on the shoreward side of the present [[Kapıdağ Peninsula]] (the classical [[Arctonnesus]]), a [[tombolo]] which is said to have originally been an island in the [[Sea of Marmara]] only to be connected to the mainland in historic times either by artificial means or an earthquake. | ||
| + | The site of Cyzicus, located on the [[Erdek]] and [[Bandırma]] roads, is protected by [[Turkey]]'s Ministry of Culture. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==History== | ||
| + | The city was said to have been founded by [[Pelasgians]] from [[Thessaly]], according to tradition at the coming of the [[Argonauts]]; later it received many colonies from [[Miletus]], allegedly in 756 BC, but its importance began only after the [[Peloponnesian War]], when the decay of Athens and Miletus set in. [[Alcibiades]] defeated the Lacedaemonians there (410 BC). The era of its Olympiads was reckoned from 135 or 139. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Owing to its advantageous position it speedily acquired commercial importance, and the gold [[stater]]s of Cyzicus were a staple currency in the ancient world till they were superseded by those of [[Philip II of Macedon|Philip of Macedon]]. Its unique and characteristic coin, the ''cyzicenus'', was worth 28 drachmae. | ||
| + | |||
| + | During the Peloponnesian War (431-404 BC) Cyzicus was subject to the [[Athens|Athenians]] and [[Lacedaemon]]ians alternately. In the naval [[Battle of Cyzicus]] in 410 during the [[Peloponnesian War]], an Athenian fleet routed and completely destroyed a Spartan fleet. At the peace of [[Antalcidas]] (387 BC), like the other Greek cities in Asia, it was made over to [[Persian Empire|Persia]]. [[Alexander the Great]] later captured it from the Persians in 334 BC and was later claimed to be responsible for the land bridge connecting the island to the mainland. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The history of the town in Hellenistic times is closely connected with that of the [[Attalid dynasty|Attalids]] of [[Pergamon]], with whose extinction it came into direct relations with Rome. Cyzicus was held for the Romans against King [[Mithridates VI of Pontus]] who besieged it with 300,000 men in 74 BC, but it withstood him stoutly, and the siege was raised by [[Lucullus]]: the loyalty of the city was rewarded by an extension of territory and other privileges. The Romans favored it and recognized its municipal independence. Cyzicus was the leading city of Northern [[Mysia]] as far as [[Troas]]. | ||
| + | [[Image:Istanbul - Museo archeol. - Auriga greco - Arcaico, sec. VI aC, da Cizico - Foto G. Dall'Orto 28-5-2006.jpg|thumb|right|280px|Bas-relief of a charioteer, late 6th century B.C.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Under [[Tiberius]], it was incorporated into the [[Roman Empire]] but remained the capital of [[Mysia]] (afterwards, [[Hellespontus]]) and became one of the great cities of the ancient world. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cyzicus was captured temporarily by the Arabs in 675. It appears to have been ruined by a series of earthquakes since 443 with the last in AD 1063. It began to be largely deserted as early as the eleventh century and the population was transferred to [[Artaki]] at least as early as the 13th century, when the peninsula was occupied by the [[Crusader]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the [[Ottoman Empire|Ottoman era]], it was part of the [[kaza of Erdek]] in the [[Brusa Vilayet|province of Brusa]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Ecclesiastical history== | ||
| + | A [[titular see]] of Asia Minor, metropolitan of the ancient ecclesiastical province of Hellespontus. As ecclesiastical metropolis of the Roman Hellespontus province, Cyzicus had a catalogue of bishops beginning with the first century; [[Michel Le Quien]] (I, 747) mentions fifty-nine. A more complete list is found in Nicodemos, in the Greek "Office of St. Emilian" (Constantinople, 1876), 34-36, which has eighty-five names. Of particular importance are the famous [[Arianism|Arian]]; [[Eunomius of Cyzicus]]; [[Saint Dalmatius]]; [[Proclus of Constantinople]] and [[Germanus of Auxerre]], who became Patriarchs of Constantinople; and Saint Emilian, a martyr in the eighth century. Another Saint who came from Cyzicus is Saint [[Tryphaena of Cyzicus]]. Tryphaena is the patron saint of the city. [[Gelasius of Cyzicus|Gelasius]], a historian of Arianism, who wrote about 475, was born at Cyzicus. [[Lequien]] (III, 941) mentions a Latin bishop in 1477. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Cyzicus is still a [[metropolitan bishop|metropolitan title]] for the Greek Orthodox, the metropolitan residing at Artake (Erdek), a little port on the western shore of the peninsula. Opposite to Artake is another port, Peramos (Perama), where an Assumptionist Father founded a Greek parish. At Panormos (Panderma), another more important port nine miles (14 km) south-east of the ruins of Cyzicus (10,000 inhabitants), there is a Catholic Armenian parish. At the Dardanelles there is also a Latin parish. It remains a Catholic titular see. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Monuments== | ||
| + | The site amid the marshes of Balkiz Serai is known as Bal-Kiz and entirely uninhabited, though under cultivation. The principal extant ruins are the walls, dating from the fourth century, which are traceable for nearly their whole extent, and the substructures of the temple of [[Hadrian]], the ruins of a Roman aqueduct and a theatre. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The picturesque amphitheatre, intersected by a stream, built in the third century B.C., was one of the largest in the world; its diameter was nearly {{convert|500|ft|m}}. Of this magnificent building, sometimes ranked among the seven wonders of the ancient world, thirty-one immense columns still stood erect in 1444. These have since been carried away piecemeal for building purposes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Colossal foundations of a temple dedicated to the Emperor [[Hadrian]] are still visible: the columns were 21.35 metres high (about 70 feet), while the highest known elsewhere, those at [[Baalbek]] in Syria are only 19.35 metres (about 63 feet). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The monuments of Cyzicus were used by the Byzantine emperor Justinian as a quarry for the building of his Saint Sophia cathedral, and were still exploited by the Ottomans. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Notable people== | ||
| + | *[[Androsthenes of Cyzicus]], 200 BC, accompanied King [[Antiochus III the Great]] to [[India]]. | ||
| + | *[[Eudoxus of Cyzicus]], 130 BC, navigator and explorer. | ||
| + | *[[Gelasius of Cyzicus]], 5th century ecclesiastical writer. | ||
| + | *[[Adrastus of Cyzicus]], a mathematician cited by [[Augustine of Hippo]] | ||
| + | *[[Theophanes the Confessor]], who began his formal religious life at the Polychronius Monastery, located near Cyzicus. | ||
| + | * [[Lala (painter)|Lala]], a female painter and sculptor, known as ''Lala from Cyzicus''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Sources and references== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==External Links== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[http://www.asiaminorcoins.com/gallery/thumbnails.php?album=487], Ancient Elenic coins of Kyzikos | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Milesian colonies]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Greek colonies in Mysia]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Roman towns and cities in Turkey]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Ancient Greek cities]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Former populated places in Turkey]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Balıkesir Province]] | ||
| + | [[Category:History of Balıkesir Province]] | ||
Revision as of 01:17, 4 January 2012
Cyzicus (Greek: Κύζικος{{#if:|
|[[Category:Articles containing {{#switch:el
|ar = Arabic
|es = Spanish
|de = German
|fr = French
|ja = Japanese
|zh = Chinese
|bg = Bulgarian
|cs = Czech
|da = Danish
|nl = Dutch
|et = Estonian
|fi = Finnish
|el = Greek
|hu = Hungarian
|ga = Irish
|grc = Ancient Greek
|la|lat = Latin
|cy = Welsh
|en|eng = explicitly cited English
|#default = {{#ifexist:Category:Articles containing Template:ISO 639 name el language text
|Template:ISO 639 name el
|non-English
}}
}} language text]]
}}, Kyzikos; Template:Lang-ota, Aydıncıḳ) was an ancient town of Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula (the classical Arctonnesus), a tombolo which is said to have originally been an island in the Sea of Marmara only to be connected to the mainland in historic times either by artificial means or an earthquake.
The site of Cyzicus, located on the Erdek and Bandırma roads, is protected by Turkey's Ministry of Culture.
Contents |
History
The city was said to have been founded by Pelasgians from Thessaly, according to tradition at the coming of the Argonauts; later it received many colonies from Miletus, allegedly in 756 BC, but its importance began only after the Peloponnesian War, when the decay of Athens and Miletus set in. Alcibiades defeated the Lacedaemonians there (410 BC). The era of its Olympiads was reckoned from 135 or 139.
Owing to its advantageous position it speedily acquired commercial importance, and the gold staters of Cyzicus were a staple currency in the ancient world till they were superseded by those of Philip of Macedon. Its unique and characteristic coin, the cyzicenus, was worth 28 drachmae.
During the Peloponnesian War (431-404 BC) Cyzicus was subject to the Athenians and Lacedaemonians alternately. In the naval Battle of Cyzicus in 410 during the Peloponnesian War, an Athenian fleet routed and completely destroyed a Spartan fleet. At the peace of Antalcidas (387 BC), like the other Greek cities in Asia, it was made over to Persia. Alexander the Great later captured it from the Persians in 334 BC and was later claimed to be responsible for the land bridge connecting the island to the mainland.
The history of the town in Hellenistic times is closely connected with that of the Attalids of Pergamon, with whose extinction it came into direct relations with Rome. Cyzicus was held for the Romans against King Mithridates VI of Pontus who besieged it with 300,000 men in 74 BC, but it withstood him stoutly, and the siege was raised by Lucullus: the loyalty of the city was rewarded by an extension of territory and other privileges. The Romans favored it and recognized its municipal independence. Cyzicus was the leading city of Northern Mysia as far as Troas.
Under Tiberius, it was incorporated into the Roman Empire but remained the capital of Mysia (afterwards, Hellespontus) and became one of the great cities of the ancient world.
Cyzicus was captured temporarily by the Arabs in 675. It appears to have been ruined by a series of earthquakes since 443 with the last in AD 1063. It began to be largely deserted as early as the eleventh century and the population was transferred to Artaki at least as early as the 13th century, when the peninsula was occupied by the Crusaders.
In the Ottoman era, it was part of the kaza of Erdek in the province of Brusa.
Ecclesiastical history
A titular see of Asia Minor, metropolitan of the ancient ecclesiastical province of Hellespontus. As ecclesiastical metropolis of the Roman Hellespontus province, Cyzicus had a catalogue of bishops beginning with the first century; Michel Le Quien (I, 747) mentions fifty-nine. A more complete list is found in Nicodemos, in the Greek "Office of St. Emilian" (Constantinople, 1876), 34-36, which has eighty-five names. Of particular importance are the famous Arian; Eunomius of Cyzicus; Saint Dalmatius; Proclus of Constantinople and Germanus of Auxerre, who became Patriarchs of Constantinople; and Saint Emilian, a martyr in the eighth century. Another Saint who came from Cyzicus is Saint Tryphaena of Cyzicus. Tryphaena is the patron saint of the city. Gelasius, a historian of Arianism, who wrote about 475, was born at Cyzicus. Lequien (III, 941) mentions a Latin bishop in 1477.
Cyzicus is still a metropolitan title for the Greek Orthodox, the metropolitan residing at Artake (Erdek), a little port on the western shore of the peninsula. Opposite to Artake is another port, Peramos (Perama), where an Assumptionist Father founded a Greek parish. At Panormos (Panderma), another more important port nine miles (14 km) south-east of the ruins of Cyzicus (10,000 inhabitants), there is a Catholic Armenian parish. At the Dardanelles there is also a Latin parish. It remains a Catholic titular see.
Monuments
The site amid the marshes of Balkiz Serai is known as Bal-Kiz and entirely uninhabited, though under cultivation. The principal extant ruins are the walls, dating from the fourth century, which are traceable for nearly their whole extent, and the substructures of the temple of Hadrian, the ruins of a Roman aqueduct and a theatre.
The picturesque amphitheatre, intersected by a stream, built in the third century B.C., was one of the largest in the world; its diameter was nearly Template:Convert. Of this magnificent building, sometimes ranked among the seven wonders of the ancient world, thirty-one immense columns still stood erect in 1444. These have since been carried away piecemeal for building purposes.
Colossal foundations of a temple dedicated to the Emperor Hadrian are still visible: the columns were 21.35 metres high (about 70 feet), while the highest known elsewhere, those at Baalbek in Syria are only 19.35 metres (about 63 feet).
The monuments of Cyzicus were used by the Byzantine emperor Justinian as a quarry for the building of his Saint Sophia cathedral, and were still exploited by the Ottomans.
Notable people
- Androsthenes of Cyzicus, 200 BC, accompanied King Antiochus III the Great to India.
- Eudoxus of Cyzicus, 130 BC, navigator and explorer.
- Gelasius of Cyzicus, 5th century ecclesiastical writer.
- Adrastus of Cyzicus, a mathematician cited by Augustine of Hippo
- Theophanes the Confessor, who began his formal religious life at the Polychronius Monastery, located near Cyzicus.
- Lala, a female painter and sculptor, known as Lala from Cyzicus.
Sources and references
External Links
- [1], Ancient Elenic coins of Kyzikos