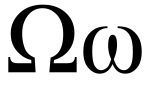Omega
From Textus Receptus
(→The symbol Ω (majuscule letter)) |
(→The symbol ω (minuscule letter)) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== The symbol ω (minuscule letter) == | == The symbol ω (minuscule letter) == | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
** Used in place of [[ん]] in Japanese typing shorthand. | ** Used in place of [[ん]] in Japanese typing shorthand. | ||
** In [[linguistics]], the [[phonological word]] | ** In [[linguistics]], the [[phonological word]] | ||
** In [[textual criticism]], the [[archetype]] of a manuscript tradition | ** In [[textual criticism]], the [[archetype]] of a manuscript tradition | ||
| - | |||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
Revision as of 08:55, 17 December 2011
Omega (majuscule: Ω, minuscule: ω; Greek Ωμέγα) is the 24th and last letter of the Greek alphabet. In the Greek numeric system, it has a value of 800. The word literally means "great O" (ō mega, mega meaning 'great'), as opposed to Omicron, which means "little O" (o mikron, micron meaning "little").[1] This name is Byzantine; in Classical Greek, the letter was called ō (ὦ), whereas the Omicron was called ou (οὖ).[2] The form of the uppercase letter derives from that of an Omicron (Ο) broken up at the side (![]() ), with the edges subsequently turned outwards (
), with the edges subsequently turned outwards (![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ).[3] The modern lowercase shape goes back to the uncial form
).[3] The modern lowercase shape goes back to the uncial form ![]() , a form that developed during the 3rd century BC in ancient handwriting on papyrus, from a flattened-out form of the letter (
, a form that developed during the 3rd century BC in ancient handwriting on papyrus, from a flattened-out form of the letter (![]() ) that had its edges curved even further upwards.[4]
) that had its edges curved even further upwards.[4]
Phonetically, the Ancient Greek Ω is a long open-mid o [ɔː], equal to the vowel of British English raw. In Modern Greek Ω represents the same sound as omicron. The letter omega is transcribed ō or simply o.
Omega (the last letter of the Greek alphabet) is often used to denote the last, the end, or the ultimate limit of a set, in contrast to Alpha, the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the New Testament book of Revelation, God is declared to be the "alpha and omega, the beginning and the end, the first and the last".[5]
Omega was also adopted into the early Cyrillic alphabet. See Cyrillic omega (Ѡ, ѡ). A Raetic variant is conjectured to be at the origin or parallel evolution of the Elder Futhark ᛟ.
The symbol ω (minuscule letter)
- Used in place of ん in Japanese typing shorthand.
- In linguistics, the phonological word
- In textual criticism, the archetype of a manuscript tradition
Notes
- 1. The Greek Alphabet
- 2. Herbert Weir Smyth. A Greek Grammar for Colleges. §1
- 3. Anne Jeffery (1961), The local scripts of archaic Greece, p.37–38.
- 4. Edward M. Thompson (1912), Introduction to Greek and Latin paleography, Oxford: Clarendon. p.144
- 5. Revelation 22:13, KJV, and see also 1:8, Greek ἐγὼ τὸ ἄλφα καὶ τὸ ὦ, ὁ πρῶτος καὶ ὁ ἔσχατος, ἡ ἀρχὴ καὶ τὸ τέλος. Or in Revelation 1:8 as seen in the Latin Vulgate Bible, the Greek is shown, surrounded by Latin: "ego sum α et ω principium et finis dicit Dominus Deus qui est et qui erat et qui venturus est Omnipotens"
- 6. Excerpts from The Unicode Standard, Version 4.0. Retrieved 11 October 2006.