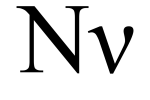Nu
From Textus Receptus
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | '''Nu''' (uppercase '''Ν''', lowercase '''ν'''; also transcribed as '''Ny'''; modern Νι ni | + | [[image:nu.png|thumb|150px|Nu]] |
| + | '''Nu''' (uppercase '''Ν''', lowercase '''ν'''; also transcribed as '''Ny'''; modern Νι ni Ni), is the 13th letter of the [[Greek alphabet]]. In the system of [[Greek numerals]] it has a value of 50. Its [[Latin Alphabet]] equivalent is N, though the lowercase resembles the Roman lowercase [[v]]. | ||
The name of the letter is written νῦ in [[Ancient Greek]] and traditional [[Modern Greek]] [[polytonic orthography]], while in [[Modern Greek]] it is sometimes written νι [ni]. In English, the name of the letter is ˈnuː or /ˈnjuː/. | The name of the letter is written νῦ in [[Ancient Greek]] and traditional [[Modern Greek]] [[polytonic orthography]], while in [[Modern Greek]] it is sometimes written νι [ni]. In English, the name of the letter is ˈnuː or /ˈnjuː/. | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 17 March 2011
Nu (uppercase Ν, lowercase ν; also transcribed as Ny; modern Νι ni Ni), is the 13th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 50. Its Latin Alphabet equivalent is N, though the lowercase resembles the Roman lowercase v.
The name of the letter is written νῦ in Ancient Greek and traditional Modern Greek polytonic orthography, while in Modern Greek it is sometimes written νι [ni]. In English, the name of the letter is ˈnuː or /ˈnjuː/.
The lower-case letter ν is used as a symbol for:
- Degree of freedom in statistics
- The spatial frequency of a wave in physics and other fields.
- Kinematic viscosity in fluid mechanics
- Poisson's ratio, the ratio of strains perpendicular with and parallel with an applied force.
- Any of three kinds of neutrino in particle physics.
- One of the Greeks in mathematical finance, known as "vega".
- The number of neutrons released per fission of an atom in nuclear physics.
- A DNA polymerase found in higher eukaryotes and implicated in Translesion Synthesis.
- Molecular vibrational mode, νx where x is the number of the vibration (a label)
- The stoichiometric coefficient
- The Greatest fixed point of a function, as commonly used in the μ-calculus
- The maximum conditioning possible for an unconditioned stimulus in the Rescorla-Wagner model