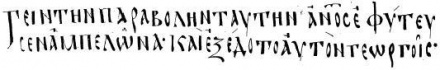Codex Cyprius
From Textus Receptus
m (Protected "Codex Cyprius" [edit=autoconfirmed:move=autoconfirmed]) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | '''Codex Cyprius''', designated by '''K<sup>e</sup>''' or '''017''' (in the [[Biblical manuscript#Gregory-Aland|Gregory-Aland]] numbering), ε 71 ([[Biblical manuscript#Von Soden|von Soden]]), is a Greek [[uncial]] [[manuscript]] of the [[Gospels]], dated [[Paleography|paleographically]] to the 9th century.< | + | '''Codex Cyprius''', designated by '''K<sup>e</sup>''' or '''017''' (in the [[Biblical manuscript#Gregory-Aland|Gregory-Aland]] numbering), ε 71 ([[Biblical manuscript#Von Soden|von Soden]]), is a Greek [[uncial]] [[manuscript]] of the [[Gospels]], dated [[Paleography|paleographically]] to the 9th century.<sup>[1]</sup> |
== Description == | == Description == | ||
Revision as of 09:18, 12 June 2015
Codex Cyprius, designated by Ke or 017 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), ε 71 (von Soden), is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Gospels, dated paleographically to the 9th century.[1]
Contents |
Description
The codex contains a complete text of the four Gospels on 267 parchment leaves (26 cm by 19 cm). It was written in one column per page, 16-31 lines per page.<ref name = Aland/>
The letters and words are not separated from one another (scriptio-continua). The uncial letters of this codex are large, upright, and compressed. In some of the pages letters are very large. It contains τιτλοι, κεφαλαια (added by a later hand), στιχοι, and Menologion. The Ammonian Sections presented, but the Eusebian Canons are absent. Itacisms is very often.
The Greek text of this codex is a representative of the Byzantine text-type.<ref>Bruce M. Metzger, Bart D. Ehrman, The Text of the New Testament: Its Transmission, Corruption, and Restoration, Oxford University Press, 2005, p. 77. </ref> Together with Codex Petropolitanus belongs to the family Π, which is in close relationship to the Codex Alexandrinus. Kurt Aland placed it in Category V.<ref name=Aland/> The text of the codex is cited in NA27.
In Mark 10:19 — phrase μη αποστερησης omitted, as in codices B (added by second corrector), W, Ψ, f1, f13, 28, 700, 1010, 1079, 1242, 1546, 2148, ℓ 10, ℓ 950, ℓ 1642, ℓ 1761, syrs, arm, geo.<ref>UBS3, p. 165. </ref> This omission is typical for the manuscript of the Alexandrian and Caesarean text-type.
In Luke 9:55-56 it has interpolation:
- στραφεις δε επετιμησεν αυτοις και ειπεν, Ουκ οιδατε ποιου πνευματος εστε υμεις; ο γαρ υιος του ανθρωπου ουκ ηλθεν ψυχας ανθρωπων απολεσαι αλλα σωσαι (but He turned and rebuked them and He said: "You do not know what manner of spirit you are of; for the Son of man came not to destroy men's lives but to save them) — as in codices: Π 1079 1242 1546 (f1 omit γαρ) (Θ f13 omit υμεις and γαρ)
History
The codex was brought from Cyprus to the Colbert Library in Paris in 1673,<ref>S. P. Tregelles, An Introduction to the Critical study and Knowledge of the Holy Scriptures, London 1856, p. 201. </ref> It was examined by Richard Simon,<ref>Simon, Histoire critique du texte du N. T. Rotterdam 1689, Kap. X, p. 101b, and Kap. XXXII, p. 407f.</ref> Mill,<ref>Mill, N. T. Gr. Küster's Ausg, Amsterdam 1710, § 1498, p. 166a.</ref> Montfaucon,<ref>Bernard de Montfaucon, Palaeoraphia Graeca, Paris 1708, p. 41, 231-233 </ref> Bianchini,<ref>Bianchini, Evang. quadr. Rom 1749, Teil 1, Vol. 2, p. </ref> Scholz,<ref>Scholz, Curae criticae .... II. De codice Cyprio u. s. w., Heidelberg 1820, p. 53-90</ref> Tischendorf in 1842 and 1949, and Tregelles in 1850.
Currently the codex is located in the Bibliothèque nationale de France (Gr. 63) in Paris.<ref name = Aland/>
See also
References
- 1. Kurt Aland, and Barbara Aland, The Text Of The New Testament: An Introduction To The Critical Editions and To The Theory and Practice Of Modern Textual Criticism, 1995, Grand Rapids, Michigan, p. 113.
- 2. Gregory, Caspar René (1900). Textkritik des Neuen Testaments, Vol. 1. Leipzig. p. 54.
- 3. Bruce M. Metzger, Bart D. Ehrman, The Text of the New Testament: Its Transmission, Corruption, and Restoration, Oxford University Press, 2005, p. 77.
- 4.^ UBS3, p. 165.
- 5. S. P. Tregelles, An Introduction to the Critical study and Knowledge of the Holy Scriptures, London 1856, p. 201.
- 6. Simon, Histoire critique du texte du N. T. Rotterdam 1689, Kap. X, p. 101b, and Kap. XXXII, p. 407f.
- 7. Mill, N. T. Gr. Küster's Ausg, Amsterdam 1710, § 1498, p. 166a.
- 8. Bernard de Montfaucon, Palaeoraphia Graeca, Paris 1708, p. 41, 231-233
- 9. Bianchini, Evang. quadr. Rom 1749, Teil 1, Vol. 2, p.
- 10. Scholz, Curae criticae .... II. De codice Cyprio u. s. w., Heidelberg 1820, p. 53-90
External links
- Codex Cyprius Ke (017): at the Encyclopedia of Textual Criticism.
Further readings
- Wilhelm Bousset, Die Gruppe K Π (M) in den Evangelien, Texte end Untersuchungen, Bd. 11, Leipzig 1894, Heft 4, S. 111-135.
- S. Lake, Family Π and the Codex Alexandrinus. The Text According to Mark, S & D V, London 1937.